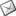Remediation laboratory involves researches in 3 areas as follows:
- Development of adsorbents from agricultural wastes for treatment of wastewater containing organic substances and heavy metals/recovery of value metals.
- Phytoremediation of wastewater/soil contaminated with heavy metals and organic substances by local Thai plant.
- Removal of color from food industry by local materials.
Our laboratory are concerned to prepare the cheap, specific and high capacity adsorbents for serving wastewater treatment by adsorption process, which is an alternative way to eliminate all of heavy metals, organic substances and highly soluble dyes. Accordingly, agricultural wastes (i.e. corncob, coir pith, shrimp shell, macadamia nut-shell, and rice husk) are appropriate to be the raw materials for preparing the special adsorbents for heavy metals, organic substances and dyestuffs. Lab scale and pilot plant are regularly tested and studied to obtain the essential parameters for supporting the operation.

Nowadays, technology for printing wastewater treatment was developed by remediation laboratory. For example, wastewater treatment of off-set, flexography and screen printing from printing industry as shown in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 Wastewater treatment of off-set, flexography and screen printing from printing industry
For example, factories which use our method for wastewater treatment

Factories which use our wastewater treatment plant

Remediation laboratory also emphasized on phytoremediation of wastewater/soil containing heavy metals and organic substances by local Thai plants. In addition, we are selecting the possibility plants that have maximum removal capacity and study on the mechanism of toxic substances uptake by hyperaccumulative plant.

In addition, the research on color removal from food industry by local materials is also studied. The aim is to develop our technology suitable in Thailand.

Objective
- To develop the adsorbents from agricultural wastes for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metals and organic substances/recovery of value metals
- To study on phytoremediation of wastewater/soil contaminated with heavy metals and organic substances by local Thai plants.
- To study on color removal from food industry by local materials.
- To create the efficiency of wastewater treatment plant and transfer the technology to the industry.
Research areas:
Development of adsorbents from agricultural wastes for treatment of wastewater contaminated with heavy metal and organic substances/color
Phytoremediation of wastewater/soil contaminated with heavy metals and organic substances/color by local Thai Plants
-
Treatment of synthetic reactive dye wastewater by narrow-leaved cattail
-
Phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by Nut grass
-
Construction wetland of ethylene glycol-contaminated wastewater by Burhead and Cyperus textilis
Removal of color from food industry by local materials
-
Decolorization of sugar syrup by bagasse fly ash/ bagasse fly ash activated carbon
-
Adsorption of melanoidin by nanochitin
-
Decolorization of rice bran oil by kaolinite
Staffs
-
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Paitip Thiravetyan
-
Dr. Parinda Suksabye
-
Mrs. Prapai Dhurakit
-
Ms. Sirikan Noonpui
-
Ms. Arunee Simaratanamongkol
-
Ms. Piyawan Leechart (Ph.D. Candidate)
-
Ms. Rujira Dolphen (Ph.D. Candidate)
Service
To consult, design and install the printing wastewater treatment (off-set, flexography and screen printing industry), color treatment (poster color, water colors, rubber-stamp ink, textile printing) and/or heavy metal-contaminated wastewater (electroplating industry).
In addition, remediation laboratory has service about academic, training and seminar to the entrepreneur and to the public.
International publications
- Ewecharoen, A., Thiravetyan, P., Wendel, E. and Bertagnolli, H. Nickel adsorption by sodium polyacrylate-grafted activated carbon, J. of Hazardous Materials (in press) (impact factor 2007 = 2.337).
- Simaratanamongkol, A., Thiravetyan, P. (2010) Decolorization of melanoidin by activated carbon obtained from bagasse bottom ash, J of Food Engineering, 96, 14-17. (impact factor 2007 = 1.848).
- Aworn, A., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2009) Preparation of CO2 activated carbon from corncob for monoethylene glycol adsorption, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,333, 19-25 (impact factor 2007 = 1.601)
- Suksabye, P., Nakajima, A., Thiravetyan, P. , Baba, Y. and Nakbanpote, W. (2009) Mechanism of Cr(V) adsorption by coir pith studied by ESR and adsorption kinetic, J. of Hazardous Materials,161, 1103-1108. (impact factor 2007 = 2.337)
- Leechart, P., Nakbanpote, W. and Thiravetyan, P. (2009) Application of ‘waste’ wood shaving bottom ash for adsorption of azo reactive dye, J. of Environmental Management, Vol. 90, 912-920. (impact factor 2007 = 1.446)
- Suksabye, P., Thiravetyan, P. , Nakbanpote, W. (2008) Column study of chromium (VI) adsorption from electroplating industry by coconut coir pith, J. of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 160, 56-62 (impact factor 2007 = 2.337)
- Aworn, A., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2008) Preparation and characteristics of agricultural waste activated carbon by physical activation having micro- and mesopores, J. of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,82,279-285. (impact factor 2007 = 2.12)
- Ewecharoen, A., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2008) Comparison of nickel adsorption from electroplating rinse water by coir pith and modified coir pith, Chemical Engineering Journal, 137, 181-188. (impact factor 2007 =1.707)
- Nilratnisakorn, S., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2007) Synthetic reactive dye wastewater treatment by Narrow-leaved cattails (Typha angustifolia Linn.): effects of dye, salinity and metals, Science of the Total Environment, 384, 67-76. (impact factor 2007 = 2.182)
- Nakbanpote, W., Goodman, B. A. and Thiravetyan, P. (2007) Copper adsorption on rice husk derived materials studied by EPR and FTIR, Colloid and Surface A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, Vol. 304, 7-13. (impact factor 2007 =1.601)
- Dolphen, R., Sakkayawong, N., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2007) Adsorption of synthetic reactive dye wastewater onto modified chitin , J. of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 145, 250-255. (impact factor 2007 =2.337)
- Suksabye, P., Thiravetyan, P. , Nakbanpote, W. and Chayabutra, S. (2007) Chromium removal from electroplating wastewater by coir pith, J. of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 141, 637-644. (impact factor 2007 = 2.337)
- Aworn, A., Thiravetyan. P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2005) Recovery of gold from gold slag by wood shaving fly ash, J. of Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 287, 394-400. (impact factor 2007 =2.309)
- Sakkayawong, N., Thiravetyan, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2005) Adsorption mechanism of synthetic reactive dye wastewater by chitosan, J. of Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 286, 36-42. (impact factor 2007 = 2.309)
- Netpradit, S., Thiravetyan, P., Nakbanpote, W. , Rattanakajhonsakul, K., Tantarawong and S., Jantarangsri, P. (2004) Waste metal hydroxide sludge as a new adsorbent, Environmental Engineering Science, Vol. 21, No. 5, 575-582. (impact factor 2007 = 0.944)
- Songkroah, C., Nakbanpote, W. and Thiravetyan, P. (2004) Recovery of silver-thiosulphate complexes by chitin, Process Biochemistry, Vol. 39, 1553-1559. (impact factor 2007 = 2.336)
- Inthorn, D., Singhtho. S., Thiravetyan, P. and Khan, E. (2004) Decolorization of basic, direct and reactive dyes by pre-treated narrow-leaved cattail (Typha angustifolia Linn.), Bioresource Technology, Vol. 94, 299-306. (impact factor 2007 =3.103)
- Netpradit, S., Thiravetyan, P. and Towprayoon, S. (2004) Adsorption of 3 azo reactive dyes by metal hydroxide sludge: Effect of temperature, pH and electrolytes Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 270, No. 2, 255-261. (impact factor 2007 =2.309)
- Netpradit S., Thiravetyan, P. and Towprayoon, S. (2004) Evaluation of metal hydroxide sludge for reactive dye adsorption in a fixed-bed column system, Water Research, Vol. 38, No. 1, 71-78. (impact factor 2007 =3.103)
- Netpradit, S., Thiravetyan, P. and Towprayoon, S. (2003) Application of ‘Waste’ metal hydroxide sludge for adsorption of azo reactive dyes, Water Research, Vol. 37, No. 4, 763-772. (impact factor 2007 = 3.103)
- Nakbanpote, W., Thiravetyan, P., and Kalambaheti, C. (2002) Comparision of gold adsorption by Chlorella vulgaris, rice husk and activated carbon, Minerals Engineering, 15, 549-552. (impact factor 2007 = 0.939)
- Nakbanpote, W., Thiravetyan, P. and Kalambaheti, C. (2000) Preconcentration of gold by rice husk ash, Minerals Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 4, 391-400. (impact factor 2007 = 0.939)
- Wilawan, S., Thiravetyan, P. and Tanticharoen, M. (2000) A possible mechanism of Zn2+ uptake by living cells of Penicillium sp., Biotechnology Letters, Vol. 22, No. 21, 1709-1712. (impact factor 2007 = 1.222)
Petty Patents
- Thiravetyan, P., Nakbanpote, W., Netpradit, S. and Thiraket, P. (2005) Wastewater containing color and/or heavy metals system and process to treatment of wastewater containing color and/or heavy metals ( Petty Patent No. 1887).
- Thiravetyan, P., Dolphen, R., Sakkayawong, N. and Nakbanpote, W. (2007) Process of modified chitin by sodium hyperchlorite (Petty Patent No. 4003).
- Thiravetyan, P., Leechart, P., Suksabye, P. and Nakbanpote, W. (2009) Process of preparation of coir pith as an adsorbent in cylinder container for treatment of heavy metal from industrial factory (Petty Patent No. 4900).
More information, please call 02-470-7536-7
|